SafeT21expressTM is designed to screen for Fetal Chromosomal Aneuploidies caused by Trisomies, Sex Chromosome Aneuploidies and Microdeletions with a minimum size of 3Mb. The test utilizes Next Generation Sequencing followed by bioinformatics analysis on both maternal DNA and cell free placental DNA found in maternal blood.
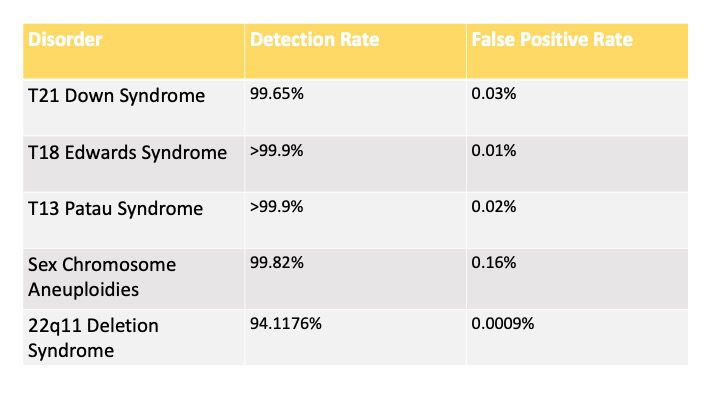
Based on safeT21expressTM internal validation data, the table below indicates the detection rates and false positive rates of the test for singleton pregnancies.
The test can detect microdeletions with a minimum size of 3Mb within the chromosomal regions responsible for 1p36 Deletion Syndrome, 2q33.1 Deletion Syndrome, Angelman Syndrome, Cri-Du-Chat Syndrome, 22q11 Deletion Syndrome (including DiGeorge Syndrome), Langer-Giedion Syndrome and Prader-Willi Syndrome. However, the above syndromes are NOT ONLY caused by microdeletions. SafeT21expressTM is only designed to detect forms of these syndromes caused by a microdeletion with a minimum size of 3Mb and cannot detect those caused by other abnormalities. When whole chromosome reduction overlapped with the above-mentioned microdeletion regions is detected, whole chromosome finding instead of microdeletion will be reported.
For twin pregnancies, the result accuracy relies on the assumption that each twin baby contributed no less than the minimum DNA requirement (4%), otherwise, there is a risk of false-negative results.
For fetal reduction / vanishing twins, the tissue of the demised fetus could persistently release DNA into the maternal circulation, which may result in test interference. Blood collection must be performed at least 4 weeks after fetal demise AND with no observable tissues remaining from the demised fetus.
Limitations of the test include:
![]() The test is a screening test, NOT a diagnostic test. A negative test result does not fully eliminate the possibility of the above-mentioned disorders. All positive results should be confirmed with invasive procedures.
The test is a screening test, NOT a diagnostic test. A negative test result does not fully eliminate the possibility of the above-mentioned disorders. All positive results should be confirmed with invasive procedures.
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
On some occasions (< 1%), despite all reasonable efforts, results may persistently be non-reportable. The following conditions are the leading factors of non-reportable results:
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
(Only applicable to Advanced Panel) Chromosomal and sub-chromosomal findings with a minimum size of 3Mb other than the aforementioned abnormalities might be reported. The advanced findings are rare and complex, insufficient validation may result in lower accuracy.






